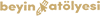POST-TRAUMATIC STRESS DISORDER
A. Exposure
B. Symptom groups B to E (symptoms that begin or worsen after the traumatic event)
C. Involuntary
D. Avoidance
E. Negative cognition and mood
F. Overstimulation
G.Additional Criteria
H. Not associated with another disorder
F. Danger of death, serious injury, accident or sexual violence
1. Experiencing a direct traumatic event(s)
2. Seeing or witnessing the event(s) that have happened to others
3. Learning that a traumatic event(s) has happened to a family member or close friend
4. Repetitive or excessive exposure to the impulsive details of the traumatic event(s)
1 or more of the following involuntary symptoms:
1. Recurrent involuntary and distressing memories of traumatic events
2. Recurrent distressing dreams, the content or emotion of which is associated with the traumatic event(s)
3. Dissociation reactions in which the person feels or acts as if the traumatic events are reoccurring
4. Experiencing intense or prolonged emotional distress at exposure to internal or external stimuli that symbolize or evoke the traumatic event(s)
5. Demonstrate distinctive physiological responses to internal or external stimuli that symbolize or evoke the traumatic event(s)
1 or more of the following avoidance symptoms:
1. Avoidance or efforts to avoid distressing memories, thoughts, or feelings related to or closely related to the traumatic event(s)
2. Efforts to avoid or avoid external reminders (people, places, conversations, activities, objects, situations) that arouse distressing memories, thoughts, or feelings about or closely related to the traumatic event(s)
At least 2 of the following symptoms:
1. Inability to remember an important aspect of the traumatic event(s)
2. Persistent and exaggerated negative beliefs about oneself, other people, or the world
3. Persistent distorted cognitions that lead the person to blame themselves or others about the causes and consequences of the traumatic event(s)
4. Persistent negative emotional state
5. Significant decrease in interest or participation in important activities
6. Feelings of detachment or alienation from others
7. Inability to consistently experience positive emotions
At least 2 of the following:
1. Angry behaviors and outbursts of anger expressed by verbal or physical aggression towards people or objects
2. Acting without restraint or engaging in self-destructive behavior
3. Stay alert at all times
4. Do not show an excessive startle response
5. Difficulty focusing
6. sleep disorder
- Longer than one month
- This disorder causes clinically significant distress or impairment in social, occupational, or functioning.
- This disorder is not attributable to the physiological effects of the use of a substance (eg, medication, alcohol) or another medical condition.